Basic Terms
| Terms | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Anison | The abbreviated form of Anime Song. It indicates the songs present in the Anime. Generally the opening (OP) and ending (ED). More info here |
| Anime Original | Content that was not present in the original source material. Can be canon or filler. |
| Canon | Canon refers to content that was not present in the original source material but is part of the anime storyline. Canon is used to expand the world-building of the anime, fix the pacing of the source material, or more character development. |
| Filler | Filler refers to content that was not present in the original source material & doesn't affect the storyline. During filler, the story doesn't get any progression. |
| Original Anime | Anime that's not an adaptation of existing material such as Manga, Light novels, picture books, etc. |
| PV | Promotional videos of the anime. Generally teaser, trailer, preview, etc. |
| Seiyuu / VA | The voice actor/actress of the anime. |
Release terms
| Terms | Meaning |
|---|---|
| OAD | Original Animation DVD. OVAs that were bundled with the source material (e.g. manga). |
| OAV | Original Animation Video. Another term for OVA. |
| ONA | Original Net Animation. Anime that was originally released on an OTT platform. |
| OVA | Original Video Animation. Anime that was originally released on a physical medium. |
| Simulcast | Simultaneous broadcast or stream of the latest episodes alongside their country of origin. |
| Simuldub | Simultaneous dub release of the latest episodes alongside their country of origin. |
Season
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Season | In Japanese TV, the broadcast schedule is divided into four seasons: Spring, Summer, Autumn, and Winter. |
| Cour | Each 13eps/season is called a cour. |
| Consecutive-cour | When the anime season spreads through 2 or more continuously without a seasonal break. Example: 2-cour anime (Kimetsu no Yaiba, The Apothecary Diaries Season 2), 3-cour (DEATH NOTE) or a 4-cour (Naruto) |
| Split-cour | When the anime season isn't continuous and has a break of one or two cours. Example: Spy x Family |
Episode Sections
| Terms | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Branding | The logo animation of studios and the distributor of the anime are shown here. The topic is really well-explained by Channel 45 |
| Recap | Recaps the previous episode(s). Generally it's found in long-running shōnen series. Example |
| Cold Opening | It's the portion of the anime before the OP. Sometimes it can be just a recap or a setup for the episode. |
| OP | Opening sequence of the anime, generally 1.5 minutes long. Depending on the episode they can also be placed closer to the middle or at the very end (example: Solo leveling s01e01). The scenes shown in them can be made for the OP only and not appear in the actual show. |
| Title Card | Also known as Title sequence. It is a part of the OP. Example |
| Mixed OP | When the OP is overlaid with the plot of the anime. |
| Eyecatch | The animated sequence before the ad break or the end of the first part. It's generally a still frame. Example |
| Insert song | A song or musical piece that occurs within the body of the anime. Example |
| ED | The ending sequence of the anime. |
| Mixed ED | Same as Mixed OP but for ED. Chainsaw-man Ep 12 & Relife Ep 13 |
| Omake | An extra portion of the episode. Generally a filler. Example |
| Preview | Shows a glimpse of the next episode which is generally an action sequence. This is also used as PV. |
File Naming
Release group
The individual or team behind the release, also called Encoder in the case of encodes. Example: SubsPlease, Erai-raws, EMBER, Yameii, etc. Sometimes, the release group name is mentioned at the end.
Source
The origin of the release, so streaming sites or different disc releases (DVD, LaserDisc, Blu-ray, etc.).
- WEB-DL: Untouched videos, downloaded from streaming sites without encoding
- WEB-Rip: Videos sourced from streaming sites that went through screen-capture and/or encoding methods
- BDISO: A disk image of a Blu-ray disc, needs to be mounted in order to be played (like other ISOs) and is used for making encodes or remuxes.
- BDMV: Short for “Blu-ray Disc Movie”, a container format used to store high-definition video, audio, and other related content on Blu-ray discs.
- Remux: Videos sourced from disc releases without encoding, making them have very high quality and file sizes.
- Encode: A video that has gone through lossless or lossy compression processes in order to save file size, also called a DVDRip or BDRip.
- Re-Encode: An encode that has gone through the process of further encoding, thus degrading in quality.
- Mini-Encode: A video where the priority is the smallest possible file size, even if the quality would greatly suffer as a result.
Resolution
The number of pixels contained in each frame, a higher value means improved quality (unless it's an upscaled release). The most common ones are 360p, 480p, 576p, 720p, 1080p, and 2160p. Most anime nowadays are made in 1080p. So, most of the 2160p anime are interpolated. This interpolation can cause artifacts, over sharpening, or aggressive denoising since it's not really possible to add details out of nothing.
Video Codec
The encoding process for the video file. The most popular encoders today are x264 (AVC) and x265 (HEVC), with the latter being newer and able to achieve higher compression rates with less quality loss.
Extra
To learn more about encoding, visit Codec Wiki.
Audio Format
Used in the encoding process for encoding audio, divided into lossless and lossy formats.
- Lossless: These retain the highest audio quality and have larger file sizes as a consequence. The most common one is FLAC.
- Lossy: These formats aim to provide good quality while keeping file sizes small. The most popular ones today are AAC, AC3, EAC3 (all commonly found in Web releases), with MP3 being found in older releases.
Subtitles
- Raw: A video without subtitles.
- Fansubs: Unofficial aka fan-made translations or an edited version of the official subtitle.
- Hardsubs: Subtitles that are burned into the frames and are part of the video track itself, can't be turned off.
- Softsubs: Subtitles that are contained on their own track inside a video file or a separate file that's loaded with the video, can be turned on or off.
File Hash
These are CRC32 codes, used to detect errors during file transmission. For example: 7BAAC64C. CRC generates a 32-bit code for each file (in hexadecimal, it's 8 digits). Fansubbers include these codes in the filename so that users can easily check whether the downloaded file is corrupted or not. If the file is corrupted, the user will receive a different code than the one written in the file name.
Video Format
The container used for the video file, with the most widely used one today being MKV, for the ability to put multiple audio/subtitle tracks in one video file. The most popular one in the past was MP4, which focused on being compatible with a wide range of devices, but was only able to have burned-in hardsubs.
Subtitle types
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Closed Captions (CC) | Also known as soft subtitles; text overlays on a video that provide translated dialogue or just audio transcription in case they're following the dub; can be turned off if not needed. |
| Open Captions (OC) | Also known as burned-in/hard subtitles; non-interactive subtitles that have been permanently 'burned' into the video file itself and can't be turned off. |
| SDH (Subtitles for the Deaf and Hard of Hearing) | A type of subtitle that includes not only dialogue but also annotations for sound effects and other audio information to aid viewers who are deaf or hard of hearing. |
| Forced Subtitles | Subtitles that automatically appear when a portion of dialogue or text is in a different language from the main audio track; they are 'forced' on screen to provide necessary translation or context. |
| Karaoke Subtitles | Karaoke subtitles highlight the lyrics in time with the Opening/Ending/Insert songs. |
Anime Production
Anime Production Process
Extra
Mentioned Kikakusho / Pitch package of Neon Genesis Evangelion.
Settai
Settai is collection of model sheets and important places (can be a house, place or anything important). The designs go through multiple stages, so they can change over time. The final drawings are used by staff as the character standard. Depending on the budget, settai can have very high details.
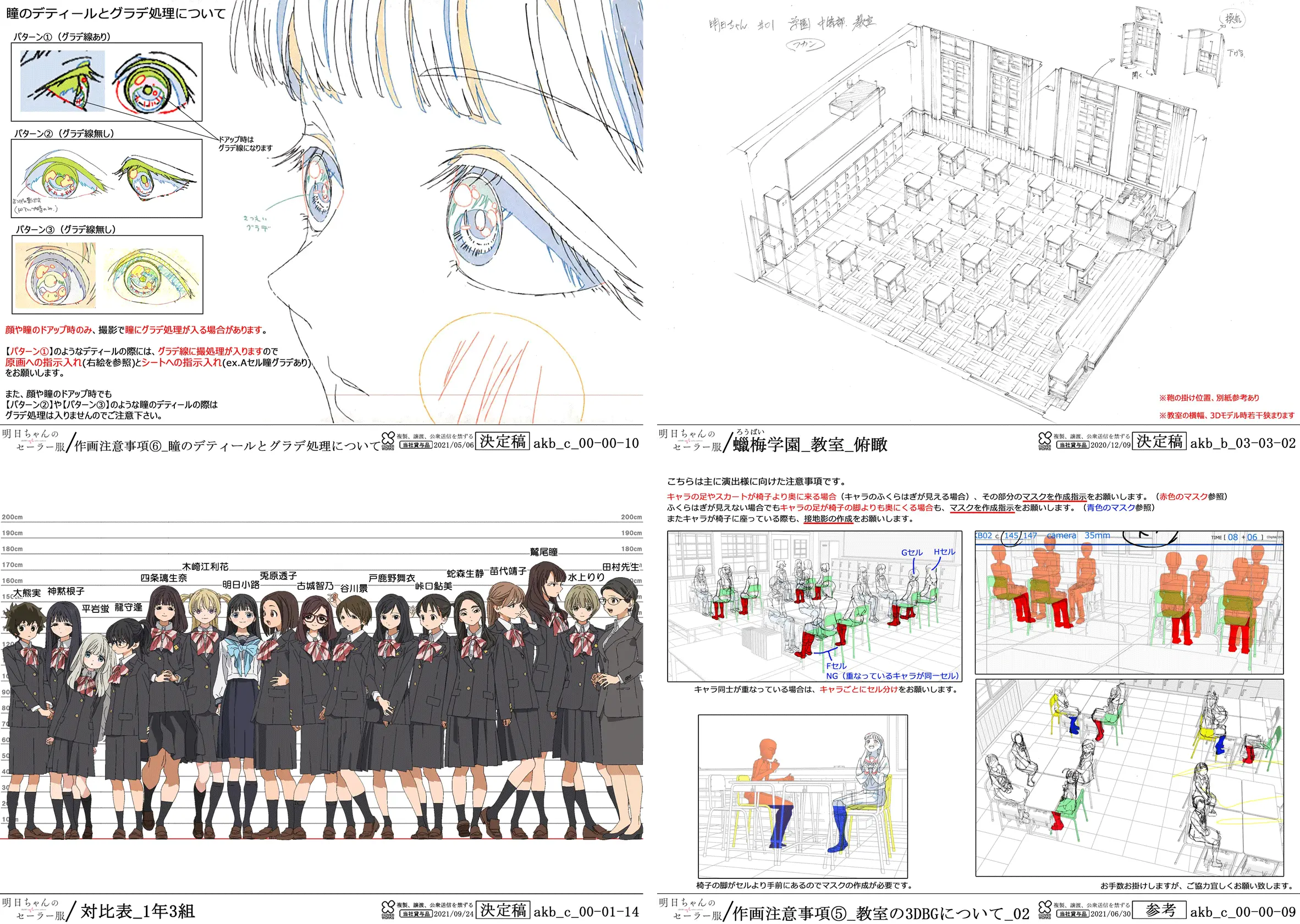
Extra
Settai Dreams & Character Design References have a lot of model sheets. Visit these sites for more examples.
E-Konte
E-Konte / storyboard shows all the sequences in rough sketches so the director can show the vision to the animators and organize accordingly. It generally has 5 columns:
- Scene & cut number
- Scene rough drawing
- Animation instructions
- Dialogue & SFX
- Time & frame number
Formatting of a storyboard can change depending on the studio and director.
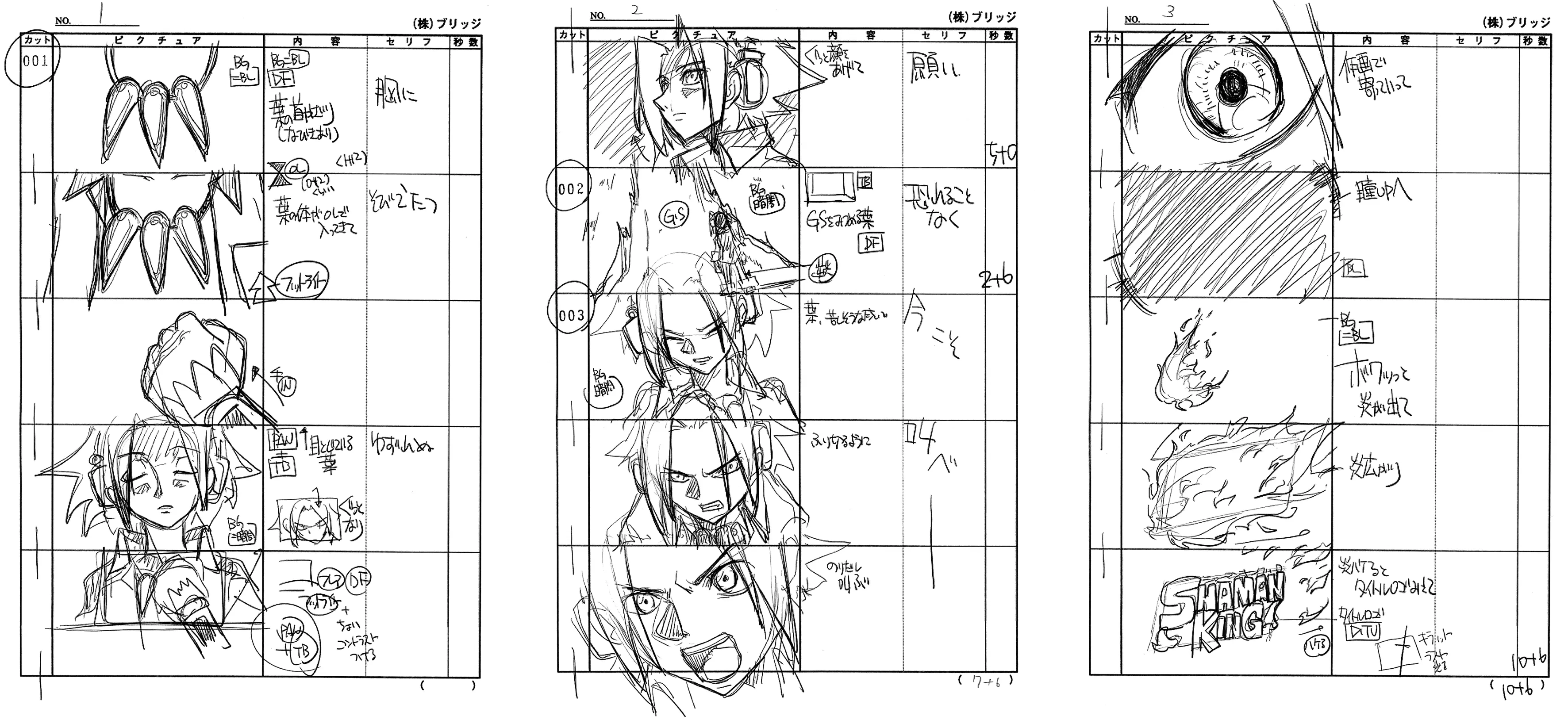
Extra
rinri posts a lot of stuff regarding storyboard. You can check out her posts there.
Genga
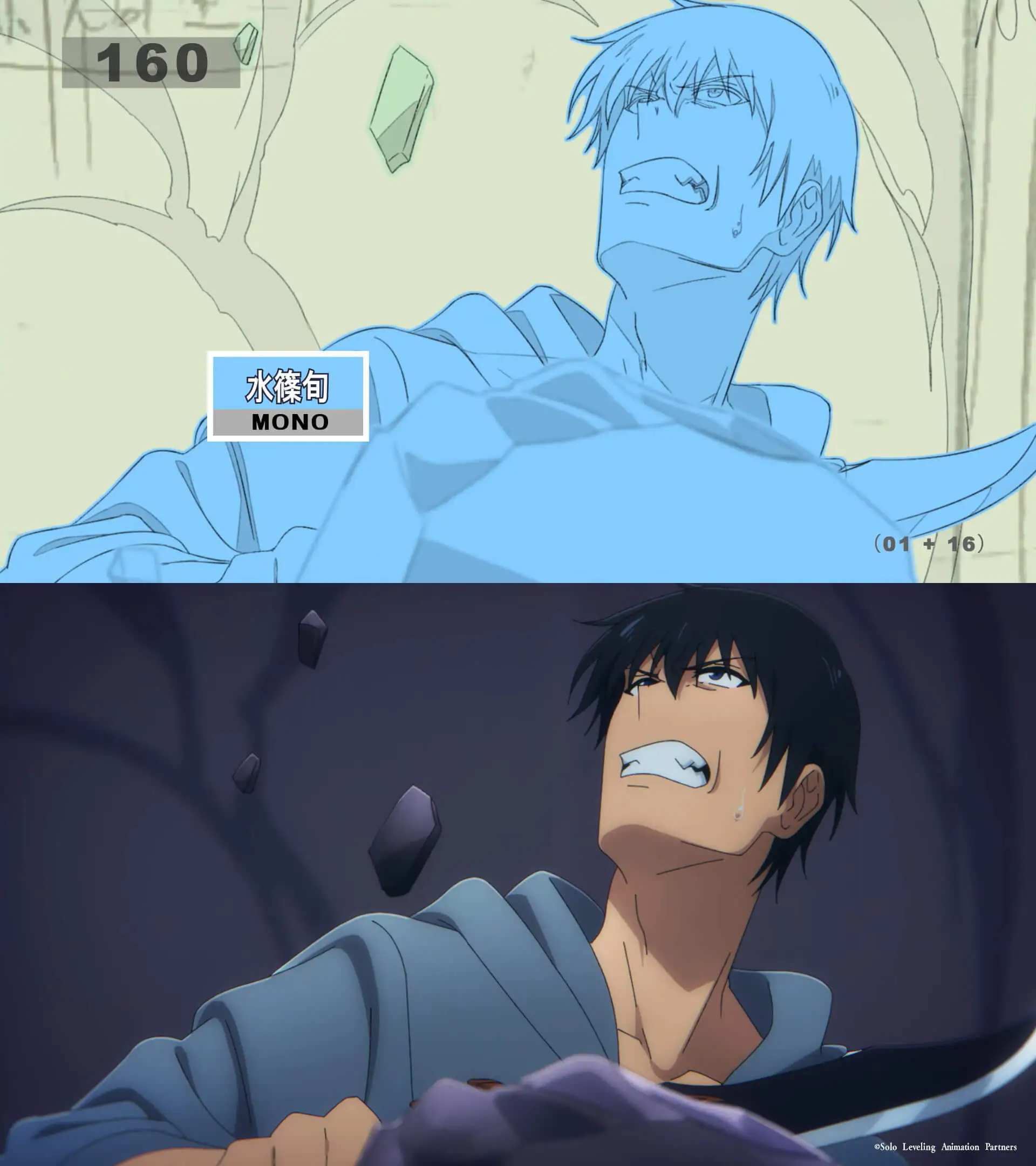
Genga means tie-down drawings or raw keyframes, drawn by genga artists. The drawn genga goes though a multi-step process.
Genga generally goes for important details of a scene. It can be just the character (or part of the character) or the character and their surrounding if the character is interacting with it. Genga doesn't generally include frame in-betweens, so it will be rough in motion by nature.
Short note
If you look at the sakuga, we can see a few numbers.
- 160 -> Scene number
- 01 -> Time (in seconds) of that scene
- 16 -> Shot number of that scene

Extra
We tried to really simplify the process. For more details, check out Dong Chang, Sakuga Foundry & Iwane Masaaki’s Animating Channel.
Timesheet
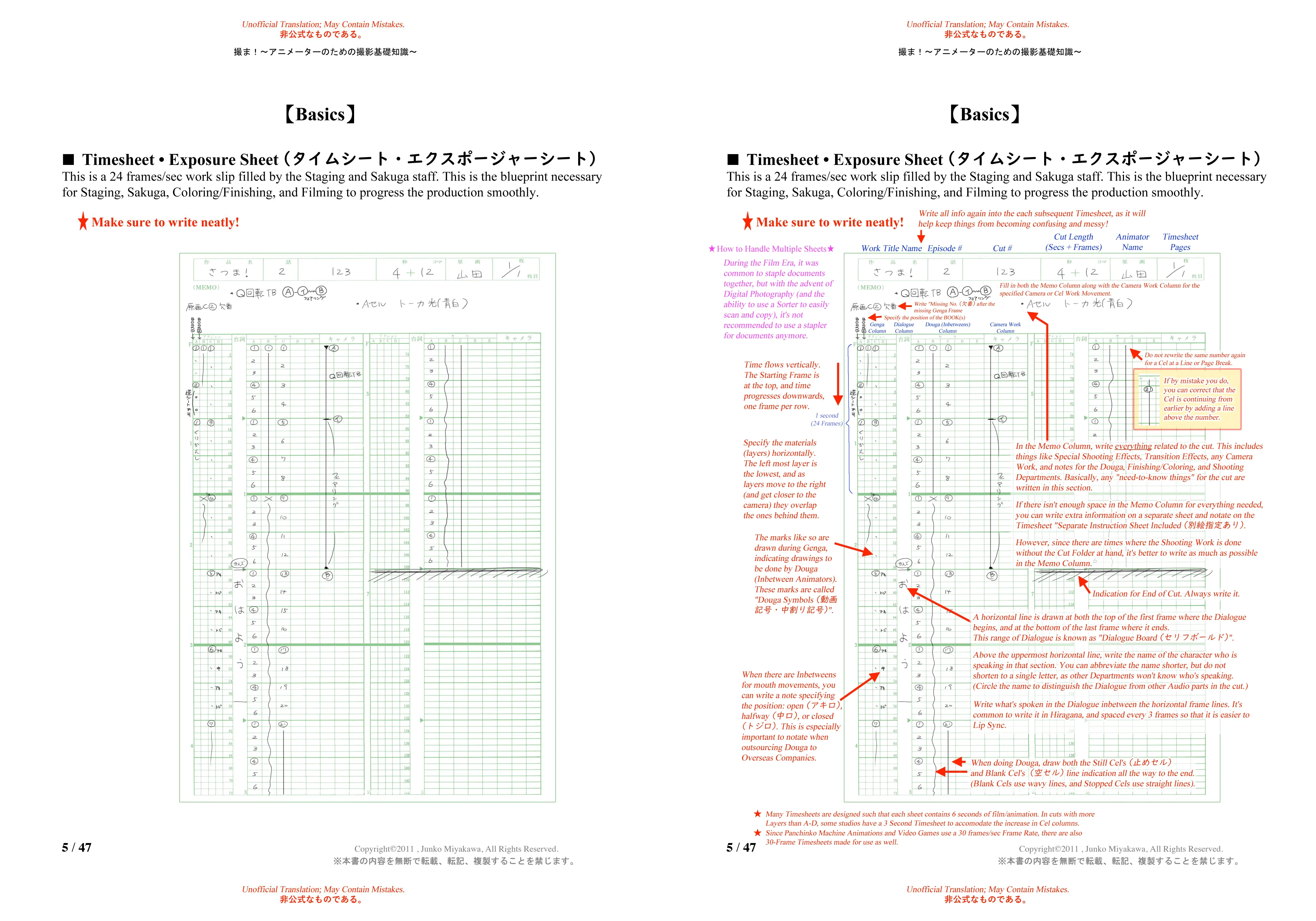
Extra
Free PDF book by Miyakawa contains a lot of info about timesheets / exposure sheets. Liss has been doing an unofficial English translation of the book. You can find a partial compiled version here and for the latest updates, click here.
Douga
More cleaned up frames, done by key animators. Dougas are way more completed and have more shading in general. The final animation looks pretty close to douga. In-betweens are also added in this step. Sometime, genga and douga can look pretty close depending on the artist.

